
AIRBORNE GAS LEAKAGE DETECTION
Lacq Gas Fied
In mid-October 2014 Dimap completed airborne trials for Total S.A. at the Lacq Gas Installation.
Methane was released in various scenarios simulating real-life leaks from open-ended lines, valves, connectors, corrosion holes, flanges, flares, and insulated tanks with breach sizes ranging from 0.5mm to 12mm.
The average duration of each release was only 5 minutes with flow rates ranging from 0.3g/s to 300g/s at a pressure of 10 bar.
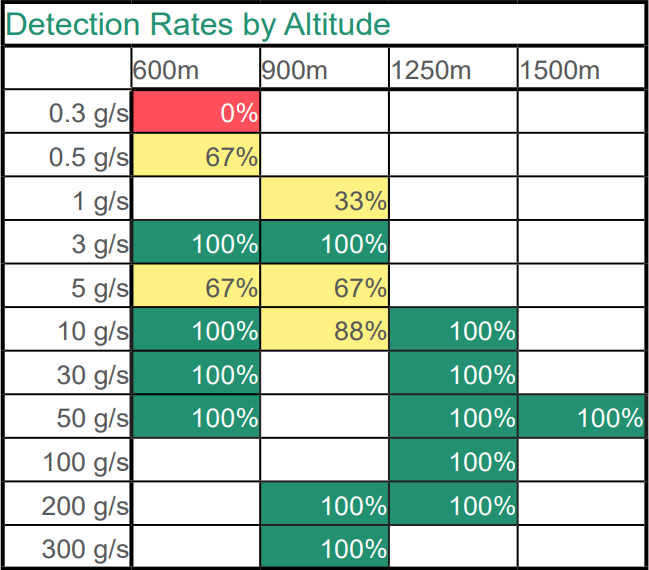
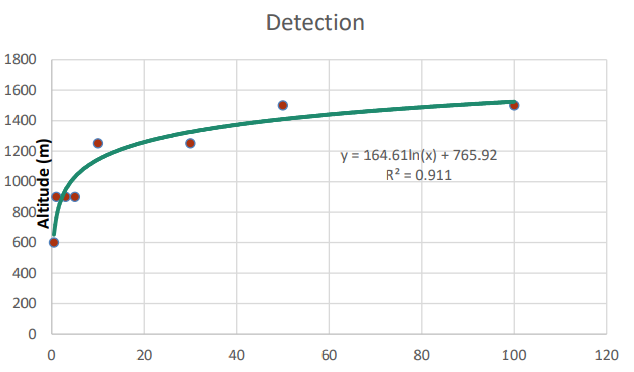
Flying our Hypercam Methane for multiple passes at 110 knots and altitudes from 600m to 1500m Dimap was able to detect an impressive 81% of all leaks with a 95% detection rate above 3g/s, and a 99% detection rate of leaks 10g/s and over.
Dimap’s method of gas leak detection utilizes airborne thermal hyperspectral sensors using a FourierTransform-Spectrometer in the thermal range to identify the location of methane absorptions and provide a concentration map.
The instrument can be installed in a helicopter or a fixed-wing aircraft. Data is preferably collected during favorable weather conditions regardless of night or day. Clear skies, low humidity, and low wind speeds are optimal weather conditions.
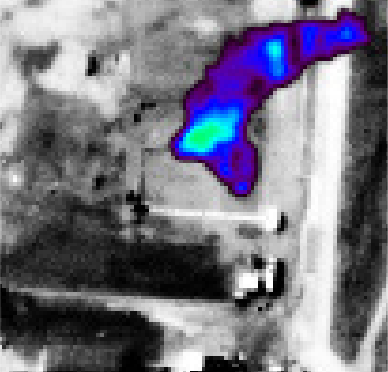

Scenarios requiring detection of methane leakages:
Safety – Dimap can help find dangerous leaks from damaged pipelines or equipment for the health of workers, the local population, and the environment.
Efficiency – Fugitive emissions have considerable financial implications as money is pouring through undetected leaks.
Compliance – Inspection, infringement checking, and regular reporting are required in most jurisdictions. Use of our aerial leak detection services can help your existing ground crews find problem areas immediately.
Deliverables to Client
1) A report identifying leakages with coordinates and pictures, illustrating the detected methane plumes directly after the flight.
2) Rectified thermal data and detection results suitable for implementation into a CAD or GIS-based management system without any further inspection.
3) High-resolution Orthorectified aerial photography which can be used to analyze encroachment into pipeline corridors by buildings, agricultural activities, and large vegetation.
